 View Large
View LargeUnderwater Explosion
Underwater Explosion analysis (UNDEX) is a critical component in the design and analysis of underwater structures such as submarines, ships, and offshore platforms. The finite element analysis is used to evaluate the response of structures to underwater explosions and to ensure that they can withstand the impact of these explosions.
Two widely used software programs for UNDEX analysis are Abaqus and LS-DYNA (which is now, Ansys LS-DYNA). Both FE software programs offer advanced capabilities for simulating and analyzing underwater explosions and their effects on structures.
Abaqus and LS-DYNA is a finite element analysis software program that provides a comprehensive suite of tools for analyzing complex structural behavior. The software is widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and defense industries. Abaqus offers a range of features for UNDEX analysis, including the ability to model fluid-structure interactions, simulate shock waves, and evaluate the dynamic response of structures to explosions, and material failure.
What is UNDEX?
An underwater explosion is a chemical phenomenon in which an explosive explodes under the surface of the water due to chemical reactions. The product of this explosion is a very hot gas (about 3000 Celsius degrees) with high pressure (14 to 28 MPa). When an explosion occurs, a wave called a pressure wave is formed, which if it is faster than the speed of sound is called a shock wave.

Underwater explosion analysis (UNDEX)
UNDEX in Abaqus
Underwater explosion analysis or UNDEX in Abaqus is a simulation technique that allows Abaqus application engineers to study the behavior and effects of explosions that occur underwater. It helps in understanding the blast wave propagation, structural response, cavitation, bubble, and damage caused by underwater explosions.
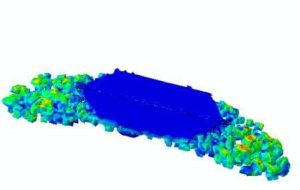
Underwater explosion analysis (UNDEX) with cavitation
Explosion Analysis
Underwater explosions are different from explosions that occur on the surface of the earth due to the characteristics of water. Water has a much higher density (about 1000 times) than air, which makes the water more difficult to move than air (higher inertia). On the other hand, water is more incompressible than air. That is, it must be at a pressure of about 100 atmospheres (about 10 MPa) to condense and increase its density. Hence it absorbs less of the explosion energy. These two things make an underwater explosion more intense than an explosion in the air.
Because an underwater explosion causes a difference in pressure and velocity, cavitation usually forms at the boundary between a solid and a fluid body, as well as at the water surface. Investigating the effect of cavitation during an underwater explosion is an issue that has been studied by many researchers. The effects of an underwater explosion depend on various factors such as the depth of the explosion, the depth of the water, the material of the explosive, and so on.
Explosion analysis
This phenomenon is more common in naval wars. Because an explosion that occurs underwater and near the bottom of a float is far more destructive than an explosion of the same size on the surface of the water. The initial destruction of the structure is formed by the shock wave caused by the explosion and then by the impact of a large volume of water and bubbles produced. If the explosive is enough and explodes just below the main bow of the ship, it will lead to the complete failure of the ship and eventually sinking.
To prevent damage from this explosion, the float must be designed to withstand it. Experimental tests related to underwater explosions are very expensive. Therefore, the best way to investigate this phenomenon is to use finite element software. Abaqus and Ansys LS Dyna software have made it possible for FE users to simulate UNDEX. There are several methods for simulating an underwater explosion, each with advantages and disadvantages. When simulating an underwater explosion, the effect of free water surface, cavitation, and bubble formation is important.
Contact our engineers in the company to order the project.
Underwater Explosion Analysis Methods
- ALE (Abaqus and Ansys LS-Dyna)
- Pressure-time equivalence method (Abaqus and LS-Dyna)
- Load_SSA in LS-Dyna software
BanuMusa R&D Services
- Surface and submarine vessels
- Explosive
- Dams