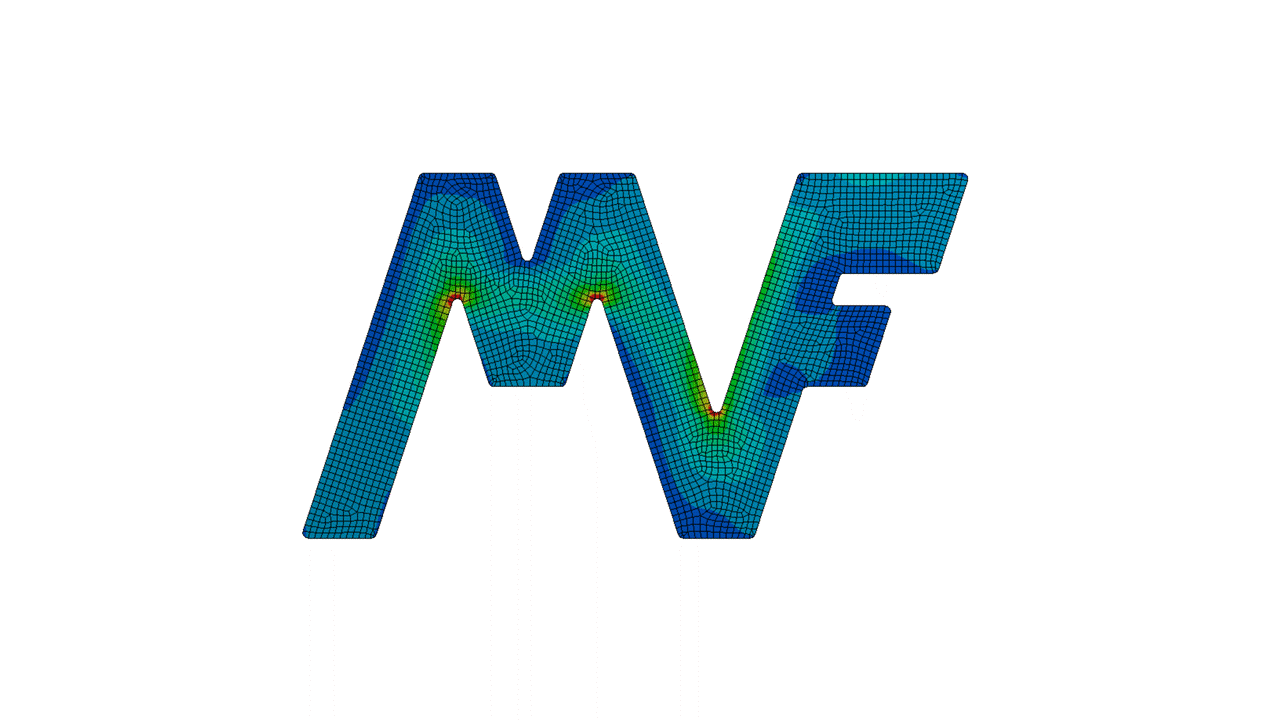Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a computer simulation technique used in engineering to analyze how a product withstands loads, heat, fluid flow, and other physical effects.
Some key concepts about FEA:
- The product geometry is divided into small pieces called elements. Elements have nodes where the pieces connect.
- The properties of the elements and loads applied are defined based on real-world conditions.
- A mesh is created by connecting the elements into a network. Finer meshes provide more accuracy.
- An equation solver calculates the effects of the applied loads on each node of the mesh.
- The node displacements, element stresses, strains, and other outputs are determined for the entire model.
- The results can be visualized through contour plots, vector plots, animations, etc.
Common Types of Finite Element Analysis
- Static structural analysis – Determines deformations and stresses from steady loads.
- Thermal analysis – Calculates temperatures and heat transfer.
- Modal analysis – Finds natural frequencies and vibration modes.
- Nonlinear analysis – Accounts for large deflections, plasticity, contact, etc.
- Fatigue analysis – Predicts fatigue life and crack propagation.
- Fracture analysis – Deals with – The initiation, propagation, and progression of cracks until final failure occurs.
- Fluid flow analysis – Models fluid dynamics and pressures.
- Shock & impact analysis – Determine how a product or system will withstand sudden accelerations, decelerations, shock, and impacts.
- Acoustic & noise analysis – It allows engineers to simulate how noise is generated within a system from vibrations and fluid flow.
- Buckling, post-buckling & collapse analysis – It determines the loads at which structures become unstable and collapse due to buckling.
- Multiphysics Simulations
- Composite Modelling and Analysis
- Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI)
Benefits of Finite Element Analysis
- Identifying weak spots and failures before manufacturing
- Optimizing designs for lighter weight, higher strength, and longer life
- Reducing physical testing needs by using virtual prototypes
- Considering many “what if” scenarios to improve designs
- Gaining insight that can be difficult or expensive to obtain otherwise
Finite Element Analysis uses the mechanics of continua to obtain approximate solutions to problems that are difficult to solve using analytical methods alone. It is a useful engineering analysis technique that provides insight to improve product designs.

Finite Element Analysis Consultancy
BanuMusa R&D one of the best-in-class Finite Element Analysis Consultancy has deep technical expertise gained from decades of hands-on experience performing structural, thermal, fluid, acoustic, and multi-physics simulations for clients across industries. We employ robust processes, the latest FEA software tools from industry leaders, and a proactive approach that identifies opportunities for design optimization, risk reduction, and cost savings. Our project management ensures studies are completed on time and budget, while effective communication delivers complex results simply. Open collaboration with clients enables knowledge transfer and strong buy-in for our recommendations. Through continuous improvement, innovation, and a focus on client outcomes, BanuMusa R&D help reduce development costs, speed time to market and improve product performance – demonstrating the tangible value of simulation tools and analysis methods for our client’s engineering and design challenges.
Here are some things to consider when hiring a finite element analysis consultancy:
- Experience – The consultancy should have extensive experience performing FEA for different industries and applications. They should have a track record of successfully supporting clients.
- Expertise – Make sure the consultancy has specialists and experts in the specific type of FEA required for your project – e.g. structural analysis, thermal analysis, acoustic analysis, multi-physics simulations, etc.
- Software tools – Check that the consultancy has access to the necessary software licenses and tools to perform the required FEA – e.g. ANSYS, ABAQUS, NASTRAN, COMSOL, etc. They should be proficient in using the relevant software.
- Methodology – A good consultancy will have robust processes and methodologies for conducting FEA studies and delivering accurate, reliable results. They should be able to explain their approach.
- Technical support – Inquire about the level of technical support the consultancy can provide. This may include answering questions, troubleshooting issues, reviewing models, and verifying results.
- Project management – How will the consultancy manage your project? They should provide timelines, deliverables, milestones, and regular progress reports. Structure and organization are important.
- Communication – The consultancy should have strong communication skills to work effectively with your team. They should be able to explain technical details clearly and concisely.
- Cost – Get quotes from multiple consultancies to compare rates. Compare based on the level of effort, deliverables, timelines, and specialist expertise required.
- References – Ask for references from previous clients the consultancy has supported. Speak to these clients to learn about their experience working with the consultancy.