Shot Peening Induced Residual Stresses – Abaqus Validation
Shot Peening Induced Residual Stresses – Abaqus Validation is a tutorial package for Abaqus users, Abaqus application engineers, and anyone who needs to learn and perform shot peening process analysis. This package contains all the required Abaqus files, and the FE results have been validated with an authoritative paper.
Results are accomplished by bombarding the surface of the component with small spherical shots made of hardened cast steel, conditioned cut-wire, and glass or ceramic beads at a relatively high velocity (40±70 m/s). After contact between the target and the shot has ceased, a small plastic indentation is formed causing stretching of the top layers of the exposed surface.
Upon unloading, the elastically stressed sub-surface layers tend to recover their original dimensions, but the continuity of the material in both zones, the elastic and the plastic do not allow this to occur. Consequently, a compressive residual stress field followed by tensile is trapped in the treated component. This surface compressive residual stress field is highly effective in preventing premature failure under conditions of cyclic loading. Fatigue failure generally propagates from the upper-most surface of the component and usually starts in a region that is subjected to high tensile stresses.
What is Shot Peening & How It Works?
Shot peening is a cold working process that involves impacting a metal surface with small abrasive particles (shot) at high velocity to produce beneficial compressive residual stresses in the surface. Also, it is used mainly to improve the fatigue life and resistance to crack initiation and propagation of metallic components.
Some benefits of shot peening are:
- Improved fatigue life – Compressive residual stresses increase resistance to crack initiation and prolong the fatigue life. Fatigue life improvement factors of 1.2x to 2x are common.
- Improved corrosion resistance – Compressive layer hinders crack initiation from corrosion pits.
- Increased yield and tensile strength
The shot used is typically steel, ceramic, or glass beads ranging from 0.1 to 2 mm in size. A larger shot produces deeper compressive zones.
Shot Peening Modeling in Abaqus
Despite its importance to the aerospace and automobile industries, little or no attention has been devoted to the accurate modeling of the process. Shot peening is a very complex process to model numerically, involving dynamic analysis of fast-moving shots impacting on a metallic component which can often have complex geometry. There are a significant number of parameters involved in shot peening that need to be controlled and regulated in order to produce a more beneficial compressive residual stress distribution within the component.
These parameters can be categorized into three groups relating to the shot, the component, and the process. The shot parameters include size, density, shape, impact velocity, rotary inertia, incident angle, and hardness. The component parameters include geometry, initial yield stress, work-hardening characteristics, and hardness.
The process parameters include mass flow rate, air pressure, angle of attack, the distance between nozzle and component, and percentage coverage. In order to control the resulting residual stress pattern in shot peened components, it would be highly beneficial to establish quantitative relationships between these parameters and residual stress characteristics.
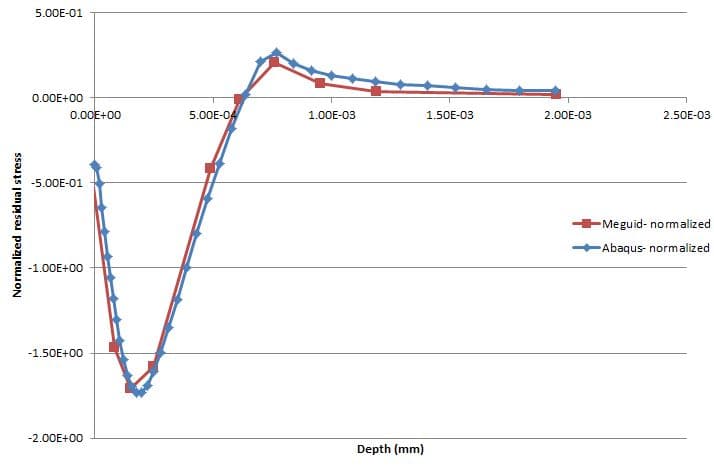
This package describes a three-dimensional dynamic finite element (FE) study of the single-shot impact on a metallic component using Abaqus/CAE software. The prediction is validated by comparison with results from the published literature by Meguid et al. (1999).
Shot Peening Induced Residual Stresses – Abaqus Validation with Mequid et al. paper
What you’ll learn
In this Abaqus training course, you will learn the following:
- How to do FEA validation with a paper
- How to model rigid bodies
- How to model elastic-plastic material
- How to use the tangential modulus in material property
- how to partition a geometry for a better mesh
- how to assign a mass to a rigid body
- how to use a dynamic explicit step
- how to select field outputs
- how to use surface-to-surface contact (Explicit)
- how to create an interaction property
- how to create boundary conditions
- how to define initial velocity for the shot peening
- how to local seeds using single and double bias
- how to use multiple processors
- how to use display group
- how to create a path
- how to export results in Excell
- how to normalize data
- how to use GetData Graph Digitizer software
Who this course is for
- Mechanical engineers who need to perform stress & fatigue analysis
- Advanced students, Ph.D. students, or researchers for their Abaqus FEA projects
- Any Abaqus application engineer who is involved with various simulation projects on a daily basis
What you’ll gain
- You will be able to perform a stress analysis of the shot peening process by Abaqus
 Abaqus Shot Peening Validation
Abaqus Shot Peening Validation
A finite element model of the experimental specimen is created in Abaqus using the same material properties and shot peening parameters. The residual stresses predicted by Abaqus are compared with the experimental measurements of the Meguid et al. paper. Material properties and/or shot peening parameters in the Abaqus model are adjusted to achieve a closer match with the experimental residual stresses.
Iterations are performed until a satisfactory agreement is reached. Once a good match is achieved, the Abaqus model is considered validated for predicting residual stresses under the specified conditions. The validated Abaqus model can now be used with confidence to predict residual stresses for the actual part under similar conditions.
The key to a successful validation is adjusting the right input parameters in Abaqus and performing enough iterations to achieve an accurate prediction of residual stresses compared to experimental measurements. This process helps calibrate the Abaqus model to mimic the real shot peening process.
With a validated model, Abaqus can be reliably used for further simulations involving changes to shot peening parameters, part geometries, materials, etc. to optimize the residual stress distribution for fatigue performance.


 Abaqus Shot Peening Validation
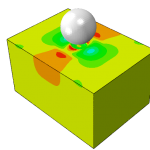
Abaqus Shot Peening Validation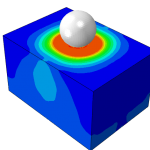
 We’re fully confident in the value and reliability of the product. If for any reason you are not completely satisfied, email us at
We’re fully confident in the value and reliability of the product. If for any reason you are not completely satisfied, email us at 























Mahenk –
These project result match nearly to the research paper, and team worked rwally good and cooperate and clear the doubts.
Engfara –
Really, I’m so satisfied about services, I asked them many addition tasks, modifications and they help me a lot. I highly recommended their services.
Engfara –
I benefited a lot from this project and it helped me pass my studies, I really recommend their services.
Mohamad Khorashad –
Thank you. We hope you continue your successful research path
Pedram Gholami –
abaqus tutorial video