Floating Ballast Water Management
The International Convention on Control and Management of Ballast Water-2004 is an international maritime treaty designed to ensure that ships comply with the standards and procedures established for the management and control of water and sediment.
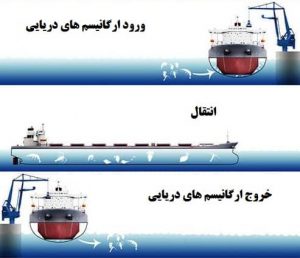
The purpose of this Convention is to prevent the spread and transmission of harmful aquatic organisms from one area to another and to prevent damage to the marine environment from high water discharge, minimizing the uptake and subsequent discharge of sediments and organisms.
Since 2014 all vessels are required to have their ballast water treatment system in accordance with the D2 standard. Existing ships need to have an approved system installed, which can cost about US $ 5 million per ship.
The International Maritime Organization or IMO has provided five guidance documents on this Convention, including
G2 Guidelines for Ballast Water Sampling, G4 Guidelines for Balancing or Ballast Water Management, and G6 Guidelines for Ballast Water Exchange.
Ballast Water
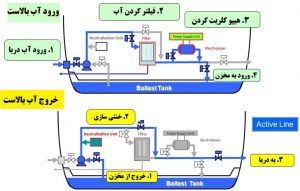
Ballast water control is essential to control stability, water line, or stress in ships. Ballast water, on the other hand, includes marine organisms and pathogens that, if they enter freshwater, cause enormous damage to the environment, human health, and resources with diverse biological characteristics.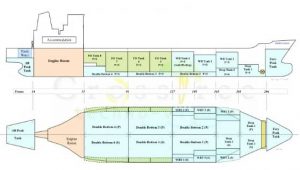
Figure 1-Ballast water tanks schematic
Ballast water Map Management
The ship’s ballast water management plan is based on B-1 by-laws of the 2004 International Convention on the Control and Management of Ballast Water. This plan will help governments, shipowners, and environmentalists minimize or completely prevent the transfer of marine organisms worldwide.
The purpose of this plan is to meet the requirements for balancing water management and management in accordance with the Balance or Ballast Water Management Guidelines and to develop floating ballast water management plans. It provides operational and standard guidance for ballast planning and management of ships and sediments and outlines safety guidelines to be followed.
Appropriate ballast water management techniques must be selected to ensure that the ballast water management practices used to comply with the Convention do not cause any further damage to the environment, human health, property or resources of any country, and vessel safety.
The Ballast Water Management Plan seeks to help governments, officials, shipowners, operators, port owners, and other stakeholders interested in preventing, minimizing and ultimately eliminating the risk of introducing harmful aquatic organisms and pathogens related to ship safety.
Keeping good records is critical to the success of a water ballast management plan. The Floating Ballast Water Management Officer is responsible for maintaining and recording the Float Ballast Water Management records and procedures.
Ballast Water Management Map (BWMS) means managing all systems involved in the ballast water process including ballast water treatment equipment, associated control equipment, monitoring equipment, and sampling facilities that exceed the standard of ballast water performance in the regulations.
 Services
Services
The requirements of the Convention on Ballast Water Management have come into force on September 1, 2009.
Our engineers at Banumusa Co., a fully-fledged IMO company, can design zero-to-100 ballast water management maps for design or built vessels.
The Executive Summary of Banumusagr Company in each vessel includes the following:
- Checking whether the vessel is exempt from the application of this Convention
- Design of filtration system according to vessel owner restrictions and location
- Design of piping and piping system
- Provide maps and documentation needed to submit to national and international rating agencies and inspectors
- Floating ballast water management plan
- Conduct training sessions for Map Executive Officers